The World Has Forgotten Two Israelis Held by Palestinian Terrorists
Where is Hisham? Where is Avera? It has been more than 3,000 days since Avera Mengistu, an Israeli citizen and member of the Ashkelon Ethiopian community, climbed over the border fence in Gaza and was captured by Hamas. His family has had zero contact with him since.David Singer: Israel set to uncork Hashemite Kingdom genie at UN
Roughly six months later, the same fate befell a 34-year-old who is part of Israel’s Bedouin community, Hisham al-Sayed, who crossed over into the terrorist-controlled enclave.What was the reason these young men ended up in the Gaza Strip? They have a long history of suffering from mental illness, and often wandered hundreds of kilometers from their homes.
On September 7, 2014, Avera was highly agitated; his mental well-being had begun to deteriorate after the tragic death of his brother. As a result, Avera left home and began to wander. Video surveillance showed that he took off and walked approximately 10 kilometers, where he was eventually spotted, unusually close to the Gaza border fence, by Israeli soldiers. The soldiers tried to get his attention; instead, he was startled and climbed over the border fence and disappeared into Gaza.
Hisham has a similar story. In the past, he had entered Jordan, the West Bank, and even Gaza, but he was always returned by security personnel who were aware of his mental status and vulnerability. In 2015, however, he was taken hostage by Hamas. Fast forward to now, and Hamas only released a video clip this year, which appears to show Hisham lying in a bed, looking dazed, and wearing an oxygen mask — the first sighting of him since he disappeared seven years ago.
The holding of Hisham and Avera is a human rights violation on several counts.
Firstly, they are civilians who have no part in the war between Israel and Hamas, and cannot be held or treated as enemy combatants.
Secondly, withholding information about captives, as Hamas has done, amounts to an “Enforced Disappearance” and is illegal under the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights, which has been signed by the Palestinians. It also goes against another piece of international law they signed, called The Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities, which provides protections for people with psycho-social, or mental health disabilities, including freedom from inhuman treatment and equal access to justice.
Finally, any detainees have the right to contact their families and receive visits from the International Committee of the Red Cross. All of these international rights are violated each moment that Hamas continues to hold Hisham and Avera hostage. Even the likes of Sarah Leah Whitson, Middle East director at Human Rights Watch, a fierce critic of Israel, has said that “Hamas’s refusal to confirm its apparent prolonged detention of men with mental health conditions and no connection to the hostilities is cruel and indefensible.”
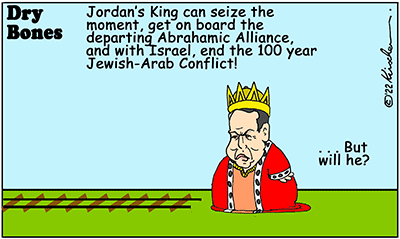
The UN stands to become totally irrelevant if it continues to refuse to discuss the Saudi Solution following Danny Danon - Israel's former ambassador to the United Nations – claiming at the first Abraham Accords Global Leadership Summit - that Saudi Arabia may be one of the next nations to normalize relations with Israel.Abdullah in the middle
Danon stated:
“We have been in contact with the Saudis for years. I worked personally with them at the United Nations on matters of regional stability and security. It’s just a matter of time before courageous leaders step out of the shadows and full peace is achieved between all the children of Abraham. .. I expect we’ll see an agreement between Israel and Saudi Arabia this year”
This was good news for those seeking an end to the 100 years-old Jewish/Arab conflict – but bad news for the UN which continues to stubbornly support the two-state solution whilst refusing to even acknowledge the existence of the game-changing Saudi Solution since its publication six months ago.
It beggars belief that on 30 November the UN General Assembly adopted five resolutions on the questions of 'Palestine' and the Middle East without one speaker uttering the words. “Hashemite Kingdom of Palestine Solution” - whose successful implementation would see the Arab populations in Gaza, part of the 'West Bank' and the wretched UNRWA camps in Lebanon and Syria becoming citizens of that newly-created territorial entity.
Cheikh Niang (Senegal) - Chair of the Committee on the Exercise of the Inalienable Rights of the Palestinian People - introduced its annual report containing developments relating to the question of Palestine between 1 September 2021 and 31 August 2022 – which contained not one reference to the Saudi Solution in its 27 pages.
Israeli Prime Minister designate Bibi Netanyahu has made his intentions crystal-clear:
“I think the big prize is peace with Saudi Arabia, which I intend to achieve if I go back into office… The rise of Israeli power facilitated the Abraham Accords, and the continual nurturing of Israeli power will also nurture a broader peace with Saudi Arabia and nearly all of the rest of the Arab world. I intend to bring the Arab-Israeli conflict to a close.”
The 2022 Saudi Solution offers Israel:
sole sovereignty in Jerusalem,
sovereignty in part of Judea and Samaria (West Bank) and
abandonment of the 74 years-old Arab claim to return to Israel
The UN must respond to the hope of peace offered by the Hashemite Kingdom of Palestine genie.
Millions of Jordanian citizens descend from families who lived in eastern Palestine when it was ruled by the British Empire or, before that, the Ottoman Empire. Others moved to Jordan, fleeing wars launched by Israel’s Arab neighbors—Jordan among them—in 1948 and 1967. In other words, millions of Jordanians identify as Palestinians.
“While Jordanian officials may not say so explicitly,” Dr. Schanzer writes, “the animosity harbored by Jordan’s Palestinian population toward Israel has a significant influence on the kingdom’s foreign policies.”
A chapter of history Israeli leaders seldom discuss publicly: When the first Arab-Israeli war came to a halt in 1949, Jordanian forces had conquered the biblical lands of Judea and Samaria (quickly renamed “the West Bank”), from which they expelled the Jewish population. Even Jews living in the Jewish Quarter of the Old City of Jerusalem were driven out, and their homes and synagogues destroyed.
Upon taking east Jerusalem in the defensive war of 1967, then-Defense Minister Moshe Dayan decided to award a Jordanian waqf (a government-controlled religious entity) authority over the two important Muslim sites—Al-Aqsa Mosque and the Dome of the Rock—that stand atop the Temple Mount, the holiest of all Jewish sites. This profound gesture of conciliation has never been fully appreciated, much less reciprocated.
Nor do Jordanians express gratitude for the essential goods Israel currently provides, for example, water (Israel is a world leader in desalination technology) and energy (40 percent of Jordan’s electricity comes from Israeli gas). Israel also cooperates closely with Jordan on “a wide range of security-related issues.”
Dr. Schanzer notes that King Abdullah, in a conversation with former U.S. National Security Advisor H.R. McMaster last May, “voiced concerns that Iranian forces in Syria could soon destabilize his country…Jordan also faces a threat from Iran-backed militias in Iraq to the north. Additional threats loom in the south, with Iranian assets reportedly operating in the Red Sea.”
Though the enemy of Jordan’s enemy should be Jordan’s friend, Dr. Schanzer expects relations with Israel to deteriorate further. He notes the king’s “unabashed distaste” for Benjamin Netanyahu, who is now forming a new government.
Netanyahu, for his part, is undoubtedly reading with distress “reports that Hamas leader Khaled Meshaal has been spending more time in Jordan with the approval of the Hashemite Kingdom.”
The king of Jordan is a moderate, modern and savvy sovereign. But without Israeli support, his future and that of his country will be precarious.
And if there is to be peace between Israelis and Palestinians, Jordan will need to join the pragmatic Arab states advocating for a new regional order, one based on stability and prosperity.
For King Abdullah to explain all this to his subjects—penetrating the fog of Palestinian irredentism and rejectionism—will not be easy. But that is his job.























.jpg)




